HSCM
- About HSCM
- Manufacturing Process
- Key Benefits
- Key Substances
- Comparative Analysis
- Research on Efficacy
- Test Reports
About HSCM
The Source of Biotechnology: Human Cord Blood Stem Cell Conditioned Media
Hucord’s Human Cord Blood Stem Cell Conditioned Media (HSCM),
a pinnacle of advanced biotechnology, offers the promise of healthier skin and new treatment possibilities.
As a key element for a healthier future for humanity, HSCM provides a unique solution for cell regeneration and recovery.
INCI/ICID
Human Cord Blood Cell Conditioned Media
INCI Monograph ID
22749
CAS No.
871903-86-5
The Significance of HSCM
HSCM is a crucial substance derived from the culture of cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, containing 151 proteins and growth factors secreted by these stem cells. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals for inflammation, wound healing, and skin disease treatment, as well as in the development of anti-aging and skin regeneration cosmetics.
Hucord will continue to lead the medical and cosmetics industries with its Human Cord Blood Stem Cell Conditioned Media (HSCM), developed through proprietary stem cell technology and maintained under world-class quality control and strict safety standards. The company is committed to ongoing growth through continuous research and development.
Manufacturing Process
-

Cord Blood Selection
-
Stem Cell Isolation
-
Stem Cell Culturing
-

HSCM Collection
-

Removal of Cellular Byproducts
-
Viral and Bacterial Testing
-

Packaging and Storage at -80°C
Key Benefits
Anti-aging Effects
-
 01
01- Prevention and Recovery of UV-Induced Skin Damage and Aging
- Repairs skin damage caused by UV radiation and inhibits the aging process.
-
 02
02- Promotion of Cell Differentiation and Proliferation
- Induces cell differentiation and proliferation to prevent aging and resist various cellular stresses.
-
 03
03- Maintenance of Skin Firmness
- Promotes fibroblast growth and activates matrix substances like collagen to maintain skin firmness.
-
 04
04- Maintenance of Skin Homeostasis
- Maintains skin’s moisture balance and regulates responses to various external environmental changes to uphold homeostasis.
Activation of Skin Regeneration
-
 01
01- Hair Growth and Follicle Formation Promotion
- Stimulates the formation of new hair follicles, preventing hair loss and promoting hair growth.
-
 02
02- Scar Minimization
- Regulates immune response during wound occurrence to minimize scar formation.
-
 03
03- Promotion of Skin Cell Growth
- Enhances the growth of epidermal cells and the basement membrane, aiding in the regeneration of damaged skin.
-
 04
04- Wound Healing
- Promotes angiogenesis, enhancing the skin’s natural healing ability for faster wound recovery.
Key Substances
Growth Factors
- IGF-1
- Regulates cell growth, development, and DNA synthesis
- Promotes the production of collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid
- IGFBP-3
- Plays a critical role in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis by regulating IGF-1 function
- Can be utilized for cancer suppression and treatment of various diseases
- IGFBP-6
- Binds to IGF-2 to regulate its physiological activities
- Exhibits anti-cancer effects by inhibiting the growth of certain cancer cells
- PDGF-AA
- Involved in angiogenesis with VEGF
- Effective for skin regeneration and hair growth
- PDGF-BB
- Promotes the proliferation and differentiation of various cells
- Plays an essential role in wound healing and tissue regeneration
- bFGF
- Involved in cell growth, morphogenesis, and tissue repair
- Stimulates fibroblasts to restore skin regeneration and maintain healthy skin
- EGF
- Stimulates cell growth and differentiation
- Maintains skin firmness and stabilizes the skin
Cytokines
- TIMP-1
- Protects against skin damage and inhibits aging caused by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) during UV exposure
- Increases collagen synthesis to reduce wrinkles
- TIMP-2
- Induces immune cells and regulates inflammatory response during tissue damage or infection
- Promotes the growth of skin fibroblasts
- GM-CSF
- Enhances the production and function of neutrophils and macrophages,
- Plays a critical role in immune and inflammatory responses.
- SCF
- Stimulates epithelial stem cells to induce cell differentiation and proliferation
- Promotes new hair follicle formation and hair growth
- IL-8
- Induces immune cells and granulocytes during tissue damage and infection
- Promotes wound healing by facilitating angiogenesis
- IL-10
- Secreted by keratinocytes during skin damage
- Regulates immunity and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects
- IL-18
- Modulates inflammatory and cell-mediated immune responses
- Applicable in treating infections, inflammatory diseases, cancer, and in vaccine development.
- IP-10
- Exhibits anti-inflammatory action and immune regulation
- Controls inflammatory responses and prevents tissue damage
- MCP-1
- Attracts monocytes and macrophages to the site of inflammation, regulating immune and inflammatory responses
- Plays a significant role in inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer
- M-CSF
- Involved in the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of macrophages
- Protects the skin from microbes and environmental pollutants
- MIP-1
- Induces immune responses during inflammation and infection
- Promotes wound healing and scar reduction
- RANTES
- Stimulates NK cell proliferation and activation
- Maintains skin homeostasis (e.g., moisture balance) by activating G-protein coupled receptors
- TGF-β1
- Promotes collagen synthesis to maintain skin firmness and reduce wrinkles
- Plays a crucial role in maintaining normal skin structure and function
Exosome
These are very small vesicles, about 50~200nm in size, generated by stem cells. They contain various factors, including RNA and proteins, similar to those found in stem cells, and contribute to the activation of skin cells.
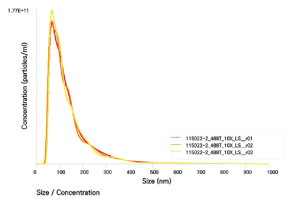
Each ml contains over 1 trillion exosomes, which significantly enhance the skin’s foundational strength. This abundance of exosomes offers remarkable benefits, including environmental protection, anti-aging effects, and anti-inflammatory action.

The high content of exosomes, which are tiny nanoparticles, allows active substances to be delivered quickly and deeply into skin cells, maximizing absorption effectiveness.
Comparative Analysis
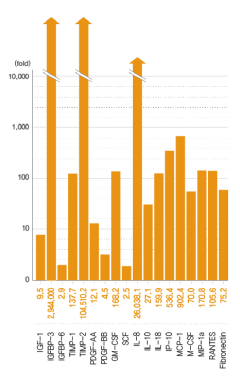
Hucord’s HSCM
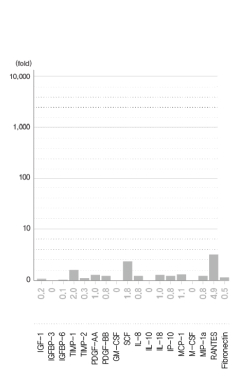
Company A / Korea

Company B / USA
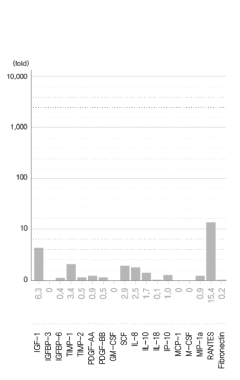
Company C / Japan
The graph shows that the growth factors and cytokines present in Hucord’s HSCM are 10,000 to 70,000 times higher than those found in other companies’ culture media.
Research on Efficacy: HSCM
The Impact of Hucord’s HSCM on Dermal Cell Proliferation Ability
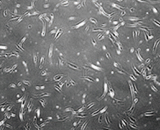
Control Group
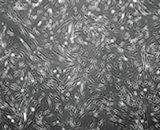
HSCM

Adipose Stem Cell Conditioned Media

Bone Marrow Stem Cell Conditioned Media
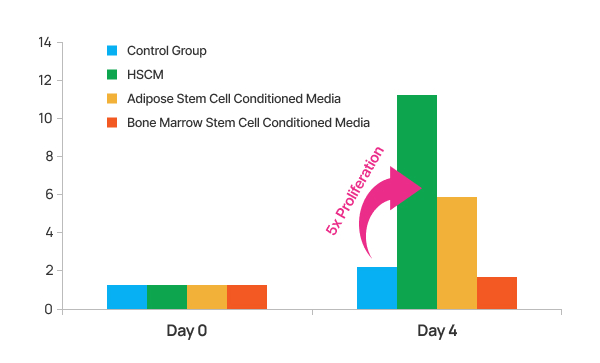
Dermal cells were cultured for four days in HSCM (Human Cord Blood Stem Cell Conditioned Media), adipose stem cell conditioned media, and bone marrow stem cell conditioned media, respectively. The results showed that bone marrow stem cell conditioned media led to a decrease in dermal cell proliferation compared to the control group, while adipose stem cell conditioned media resulted in approximately twice the proliferation. In contrast, HSCM demonstrated more than a fivefold increase in proliferation compared to the control group.
Comparison of Dermal Cell Proliferation Ability Between HSCM and Other Companies’ Stem Cell Conditioned Media

Control Group

HSCM

Company A (USA)
Company B (Korea)
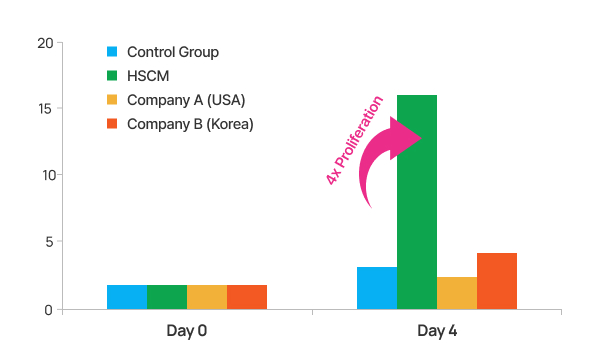
After culturing dermal cells for four days with stem cell conditioned media from various companies, Company A (USA) showed no dermal cell proliferation, while Company B (Korea) demonstrated proliferation similar to the control group. In contrast, HSCM resulted in a significant increase in proliferation, showing over four times the growth compared to the control group.
- Collagen Synthesis and Inhibition of Degradation
-
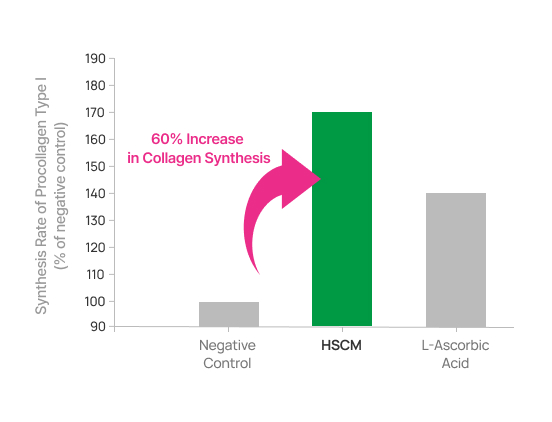
When Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid), known for its superior ability to synthesize collagen, was supplied to skin dermal cells, collagen synthesis increased by 40% compared to the control group. However, when HSCM was supplied, collagen synthesis was confirmed to be over 60%, which is 20% higher than with Vitamin C.
Collagen: A protein that forms the support layer of skin cells and is crucial for skin elasticity and wrinkle improvement.
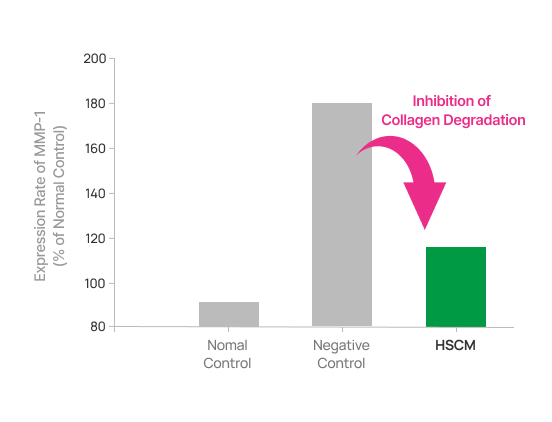
- Inhibition of MMP-1 Synthesis
-
When dermal cells were exposed to UV radiation, MMP-1 levels increased by over 80% compared to the non-irradiated control group. However, when dermal cells were exposed to UV radiation in the presence of HSCM, the synthesis of MMP-1 was significantly reduced to 20%. This suppression of MMP-1 helps inhibit collagen breakdown in dermal cells, thereby maintaining collagen levels in the skin.
MMP-1: This is a protein that promotes collagen degradation, leading to reduced collagen levels in the skin and contributing to the formation of wrinkles.
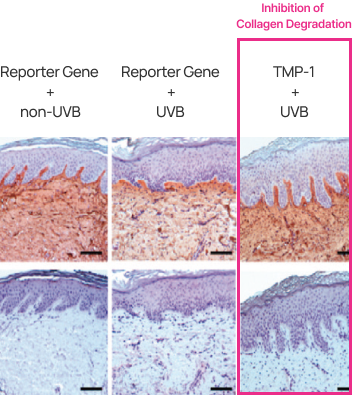
When TIMP-1 was administered, collagen IV maintained abundant continuity along the epidermal-dermal junction and blood vessels. In contrast, the control group showed a significant reduction in collagen and a loss of continuity.
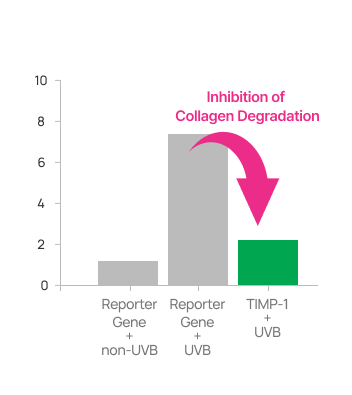
The activity of MMP-1 and MMP-9 was significantly inhibited by TIMP-1.
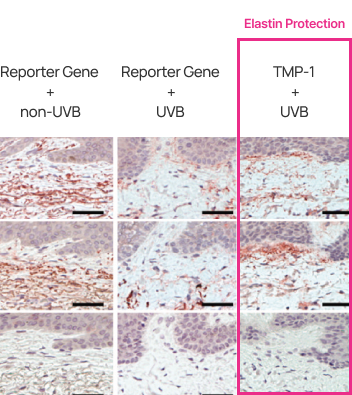
In skin tissue treated with TIMP-1, the protective effect on elastin fibers was clearly observed.
Test Reports
HSCM Safety Test Report
Safety Standards for Human Cell and Tissue Conditioned Media
-

Completion of 11 Safety Evaluation Tests
-

Completion of Quality and Facility Inspections

Single-Dose Toxicity Test

Repeated-Dose Toxicity Test

Primary Skin Irritation Test

Ocular Mucosa Irritation Test

Skin Sensitization Test

Phototoxicity Test

Photosensitization Test

Genetic Reverse Mutation Test

Genetic Chromosomal Aberration Test

Genetic Micronucleus Test

Human Patch Test

Virus Test

Cultivation Facility and Environmental Management

